H Engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
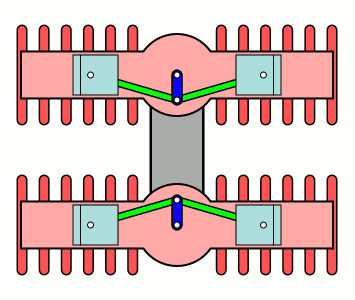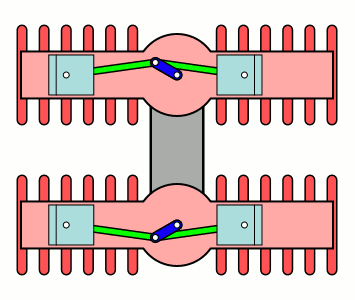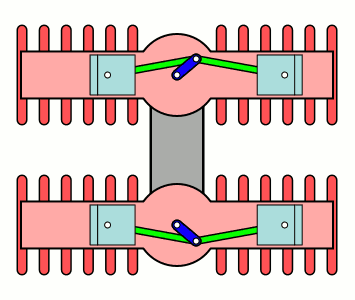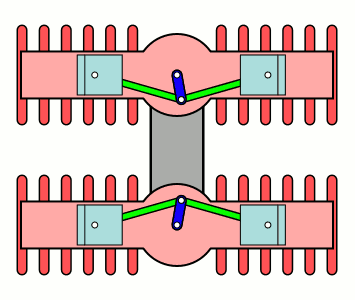 An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate
An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate
 * Lycoming, US
**
* Lycoming, US
**
File: BRM H16 engine.jpg ,
 The
The
 An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate
An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate flat engines
Flat or flats may refer to:
Architecture
* Flat (housing), an apartment in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia and other Commonwealth countries
Arts and entertainment
* Flat (music), a symbol () which denotes a lower pitch
* Flat (soldier), ...
(complete with separate crankshafts), most often geared to a common output shaft. The name "H engine" is due to the engine blocks resembling a letter "H" when viewed from the front. The most successful "H" engine in this form was the Napier Dagger
The Napier Dagger was a 24-cylinder H-pattern ''(or H-Block)'' air-cooled engine designed by Frank Halford and built by Napier before World War II. It was a development of the earlier Napier Rapier.
Design and development
The H-Block has a ...
and its derivatives. The name was also applied to engines of the same basic layout, but rotated through 90 degrees—most famously the Napier Sabre series. A variation on the "H" theme were the Fairey Prince (H-16) & Fairey P.24 Monarch, where the two engines retained separate drives, driving Contra-rotating propellers
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers, also referred to as CRP, coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propell ...
through separate concentric shafts. Although successful, they only existed in prototype form.
The H engine is a relatively rare layout, with its main use being in aircraft engines during the 1930s and 1940s. The 1966 Lotus 43
The Lotus 43 was a Formula One racing car designed by Colin Chapman for the 1966 season. Hampered by its heavy and unreliable BRM engine, it won only one race, the 1966 United States Grand Prix.
Concept
The Lotus 43 was partially based on th ...
Formula One car used a BRM
British Racing Motors (BRM) was a British Formula One motor racing team. Founded in 1945 and based in the market town of Bourne in Lincolnshire, it participated from 1951 to 1977, competing in 197 grands prix and winning seventeen. BRM wo ...
16-cylinder H engine, and an 8-cylinder H engine was used for powerboat racing in the 1970s.
Design
The benefits of an H engine are the ability to share common parts with the flat engine upon which it is based, and the goodengine balance
Engine balance refers to how the forces (resulting from combustion or rotating/reciprocating components) are balanced within an internal combustion engine or steam engine. The most commonly used terms are ''primary balance'' and ''secondary bala ...
which results in less vibration (which is difficult to achieve in many other types of four-cylinder engines).
However, H engines are relatively heavy and have a high centre of gravity. The latter is not only due to the second crankshaft being located near the top of the engine, but also the engine must be high enough off the ground to allow clearance underneath for the exhaust pipes.
The U engine
A U engine is a piston engine made up of two separate straight engines (complete with separate crankshafts) placed side-by-side and coupled to a shared output shaft. When viewed from the front, the engine block resembles the letter "U".
Although ...
layout uses a similar concept, placing two straight engines side-by-side.
History
Aircraft engines
 * Lycoming, US
**
* Lycoming, US
**Lycoming H-2470
The Lycoming XH-2470 was an H engine for aircraft designed and developed by Lycoming Engines in the 1930s. Although the engine was flown in an aircraft, it was not fitted to any aircraft selected for production. It was derived from the Lycoming O ...
H-24 "hyper engine
The hyper engine was a 1930s study project by the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) to develop a high-performance aircraft engine that would be equal to or better than the aircraft and engines then under development in Europe. The project goal ...
" (1930s) 2,300 hp
*Fairey Aviation
The Fairey Aviation Company Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer of the first half of the 20th century based in Hayes in Middlesex and Heaton Chapel and RAF Ringway in Cheshire. Notable for the design of a number of important military a ...
, UK
** Fairey Prince (H-16) (1939) – 1,500 hp
**Fairey Monarch
The Fairey P.24 Monarch was a British experimental 2,000 hp (1,490 kW) class H-24 aircraft engine designed and built by Fairey in the late 1930s. The engine did not go into production.
Design and development
The P.24 Monarch was a 24-cyli ...
(1939) – H-24 2,240 hp
* Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz DZ 720 – H-32, 102.9 litres diesel
* D. Napier & Son, UK.
**Napier Rapier
The Napier Rapier was a British 16-cylinder H pattern air-cooled aero engine designed by Frank Halford and built by Napier & Son shortly before World War II.
Design and development
The Rapier was the first of Napier's H cylinder engines. The ...
(1929) – H-16 air-cooled vertical, 8.83 litres 340 hp
**Napier Dagger
The Napier Dagger was a 24-cylinder H-pattern ''(or H-Block)'' air-cooled engine designed by Frank Halford and built by Napier before World War II. It was a development of the earlier Napier Rapier.
Design and development
The H-Block has a ...
(1934) – H-24, air-cooled vertical, 16.85 litres 890 hp, a development of the Rapier
** Napier Sabre (1938) – H-24, water-cooled horizontal sleeve valves, 36.7 litres 3,500 hp.
* Pratt & Whitney, US
** XH-2240 - H-24, liquid-cooled,
** XH-2600 - H-24, liquid-cooled,
** XH-3130 - H-24, liquid-cooled,
** XH-3730 - H-24, liquid-cooled,
*Rolls-Royce Eagle
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of oth ...
(1944) – H-24, 46.2 litres, 3,200 hp.
Formula One racing engines
TheBritish Racing Motors
British Racing Motors (BRM) was a British Formula One motor racing team. Founded in 1945 and based in the market town of Bourne in Lincolnshire, it participated from 1951 to 1977, competing in 197 grands prix and winning seventeen. BRM wo ...
(BRM) H-16 Formula One engine won the 1966 US Grand Prix in a Lotus 43
The Lotus 43 was a Formula One racing car designed by Colin Chapman for the 1966 season. Hampered by its heavy and unreliable BRM engine, it won only one race, the 1966 United States Grand Prix.
Concept
The Lotus 43 was partially based on th ...
driven by Jim Clark. It was also used by the unsuccessful 1966 BRM P83
The BRM P83 was a Formula One racing car designed by Tony Rudd and built by British Racing Motors for the new engine regulations of 1966. It used a highly unorthodox H16 engine which caused problems throughout the car's racing life, and despite ...
car driven by Graham Hill and Jackie Stewart. As a racing-car engine it was hampered by a high center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
, and it was heavy and complex, with gear-driven twin overhead cams for each of four cylinder heads, two gear-coupled crankshafts, and mechanical fuel injection.
BRM
British Racing Motors (BRM) was a British Formula One motor racing team. Founded in 1945 and based in the market town of Bourne in Lincolnshire, it participated from 1951 to 1977, competing in 197 grands prix and winning seventeen. BRM wo ...
H-16 engine (64-valve version)
File: BRM H16 in P83.jpg , BRM H-16 engine in a 1966 BRM P83
The BRM P83 was a Formula One racing car designed by Tony Rudd and built by British Racing Motors for the new engine regulations of 1966. It used a highly unorthodox H16 engine which caused problems throughout the car's racing life, and despite ...
Motorcycle engines
Brough Superior Golden Dream
The Brough Superior Golden Dream was designed and built by George Brough in Nottingham, England, in 1938. With its distinctive gold finish, this was to be the ultimate Brough Superior but production was stopped by the outbreak of War in 1939.
...
motorcycle, first shown in 1938. A 1,000 cc H-4 design and a few units were produced in early 1939. Any development planned was interrupted by World War II and subsequent years of austerity.
Wooler
Wooler ( ) is a small town in Northumberland, England. It lies on the edge of the Northumberland National Park, near the Cheviot Hills. It is a popular base for walkers and is referred to as the "Gateway to the Cheviots". As well as many shops ...
built a motorcycle prototype with a similar configuration to the Brough Superior Golden Dream and exhibited it at the British International Motor Show
The British International Motor Show is an annual motor show held by the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders between 1903 and 2008 in England, and as The British Motor Show since 2021 by Automotion Events.
Initially held in London at T ...
at Earls Court Exhibition Centre
Earls Court Exhibition Centre was a major international exhibition and events venue just west of central London. At its peak it is said to have generated a £2 billion turnover for the economy. It replaced exhibition and entertainment grounds, ...
in 1948 and again in 1951. This was replaced by a flat-four engined prototype at the 1953 show.
Powerboat racing engines
German firm Konig, who specialised in racing outboard motors, built a few 1000cc H-8s in the 1970s, which were basically two of their VC500 flat fours mounted one above the other, with the direction of rotation reversed on one of them. Each half of the engine was a water cooled 2-stroke with rotating disc valve driven by a toothed belt via two 45/90 degree pulleys, plus two siamesed expansion chamber exhausts, fed by two single choke carbs. Both cylinders at each end of each engine fired at the same time, hence the siamesed exhausts for each pair.Other engines named "H"
Subaru has marketed itsflat-four
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, ...
and flat-six
A flat-six engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-six, is a six-cylinder piston engine with three cylinders on each side of a central crankshaft. The most common type of flat-six engine is the boxer-six engine, where each pair of opposed cy ...
engines as "H4" and "H6" respectively. The letter "H" in this case refers to "horizontally-opposed", an alternative term for flat engines; these engines can also be said to look like a "H" or conjoined "H"s, albeit from the top and in schematic form.
The Saab H engine
The Saab H engine is a redesign of the Saab B engine, which in turn was based on the Triumph Slant-4 engine.
Despite the name it is not an H engine or horizontally opposed engine, but a slanted inline-4. The H engine was introduced in 1981 in ...
is a straight-four engine produced from 1981 to 2009. The letter "H" represents "high compression".
References
{{Piston engine configurations Piston engine configurations Engines by cylinder layout